Decision tables, also known as logic tables, have been used for centuries to represent logic in a tabular form. They continue to be a processing method of choice because they provide a quick and easy way to read, understand and execute procedures.
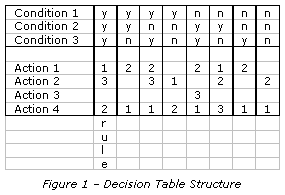
This illustrates how to understand the various components of a decision table.
A decision table is a map representing the relationships of combinations of conditions to combinations of actions. The first combination of conditions to actions are read from top to bottom from the rule column as: if Condition 1 is true and Condition 2 is true and Condition 3 is true then do Action 1 and then do Action 4 and then do Action 2.
